What is EFK
EFK is the acronym for three open source projects
Elastic , Fluentd, Kibana.
Fluentd is a log shipper and data processing pipeline that ingests data from multiple sources simultneously, transforms it, and then sends it to Elasticsearch.
Elasticsearch is a search and analytics engine. Kibana lets users
visualize data with charts and graphs in Elasticsearch.
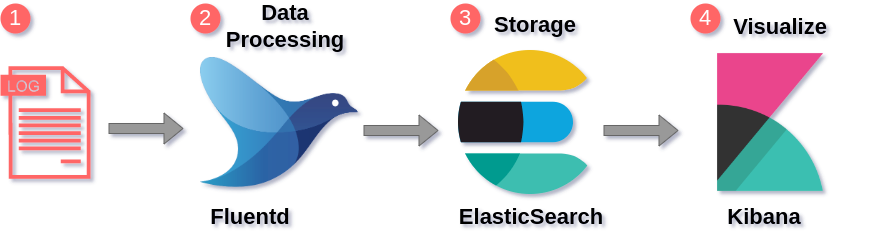
EFK Stack Architecture
Simple architecure of EFK Stack
Logs: Server logs that need to be analyzed are
identified.Fluentd: Deployed as daemonset as it need to
collect the container logs from all the nodes.It connects to the
Elasticsearch service endpoint to forward the logs.Elastic Search: Deployed as statefulset as it holds
the log data. We also expose the service endpoint for Fluentd and kibana
to connect to it.Kibana: Deployed as deployment and connects to
elasticsearch service endpoint.
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a NoSQL database. It is based on Lucence Search
engine, and it is built with RESTful APIs. It is often simple
depolyment, maximum reliabilty, and easily manageable. it also offers
advanced queries to perform detail analysis and stores all the data
centrally. It is helpful for executing a quick search of the documents.
Elasticsearch also allows you to store, search and analyze big
volume of data.It is mostly used as the underlying engine which powers
applications that completes search requirements. It has been adopted in
search engine platforms for modern web and mobile applications. Apart
from quick search, the tool also offers complex analytics and many
advanced features.
Features
- Open source search server is written using java
- Used to index any kind of heterogeneous data
- Has REST API web-interface with JSON output
- Full-Text Search
- Near Real TIme(NRT) search
- Sharded,replicated searchable,JSON document store
- Schema-free, REST & JSON based distributed document store
- Multi-language & Geolocation support
Advatages
Store schema-less data and also creates a schema for your data
Manipulate your data record by record with the help of
Multi-document APIsPerform filtering and querying your data for insights
Based on Apache Lucene and provides RESTful API
Provides horizontal scalability, reliability, and multitentant
capability for real time use of indexing to make it faster searchHelps you to scale vertically and horizontally
Fluentd
Fluentd is an efficient log aggregator. It is written in Ruby, and
scales very well. For most small to medium sized deployments, fluentd is
fast and consumes relatively minimal resources. “Fluent-bit”, a new
project from the creators of fluentd claims to scale even better and
has an even smaller resource footprint. For the purpose of this
discussion, lets focus on fluentd as it is more mature and more widely
used.
Fluentd scraps logs from a given set of sources, processes them
(converting into a structured data format) and then forwards them to
other services like Elasticsearch, object storage etc. Fluentd is
especially flexible when it comes to integrations – it works with 300+
log storage and analytic services.
- Fluentd gets data from multiple sources.
- It structures and tags data.
- It then sends the data to multiple destinations, based on matching
tags
Advantages
Fluentd provides both active-active and active-passive deployment
patterns for both availability and scale.Fluentd can forward log and event data to any number of additional
processing nodesTagging and Dynamic Routing with Fluentd
Larger Plugin Library with Fluentd
It uses less memory approx ~40MB
Kibana
Kibana is a data visualization which completes the EFK stack. This
tool is used for visualizing the Elasticsearch documents and helps
developers to have a quick insight into it. Kibana dashboard offers
various interactive diagrams, geospatial data, and graphs to visualize
complex queries.
It can be used for search, view, and interact with data stored in
Elasticsearch directories. Kibana helps you to perform advanced data
analysis and visualize your data in a variety of tables, charts, and
maps.
In Kibana there are different methods for performing searches on your
data.
Advantages and
Disadvantages of Kibana
Easy visualization
Fully integrated with Elasticsearch
Offers real-time analysis, charting, summarization, and debugging
capabilitiesProvides instinctive and user-friendly interface
Allows sharing of snapshots of the logs searched through
Permits saving the dashboard and managing multiple dashboards
kubernetes configs
Elastic Search State-full
set
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: elasticsearch
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
selector:
app: elasticsearch
# clusterIP:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 9200
name: rest
targetPort: 9200
nodePort: 31000
- port: 9300
name: inter-node
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: es-cluster
spec:
serviceName: elasticsearch
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: elasticsearch
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
containers:
- name: elasticsearch
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.6
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: rest
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9300
name: inter-node
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
env:
- name: cluster.name
value: k8s-logs
- name: node.name
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: discovery.seed_hosts
value: "es-cluster-0.elasticsearch,es-cluster-1.elasticsearch,es-cluster-2.elasticsearch"
- name: cluster.initial_master_nodes
value: "es-cluster-0,es-cluster-1,es-cluster-2"
- name: ES_JAVA_OPTS
value: "-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
initContainers:
- name: fix-permissions
image: busybox
command:
["sh", "-c", "chown -R 1000:1000 /usr/share/elasticsearch/data"]
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
- name: increase-vm-max-map
image: busybox
command: ["sysctl", "-w", "vm.max_map_count=262144"]
securityContext:
privileged: true
- name: increase-fd-ulimit
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "ulimit -n 65536"]
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: data
labels:
app: elasticsearch
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
storageClassName: "local-path"
resources:
requests:
storage: 30GiFluentd Daemon set
#https://github.com/fluent/fluentd-kubernetes-daemonset
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: default
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: fluentd
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- namespaces
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: fluentd
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: fluentd
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: fluentd
namespace: default
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-logging
version: v1
spec:
serviceAccount: fluentd
serviceAccountName: fluentd
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
effect: NoSchedule
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule
containers:
- name: fluentd
image: fluent/fluentd-kubernetes-daemonset:v1.14.6-debian-elasticsearch7-1.1
env:
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
value: "192.168.10.120"
- name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
value: "31000"
# - name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_SCHEME
# value: "http"
# - name: FLUENT_CONTAINER_TAIL_PARSER_TYPE
# value: "cri"
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: fluentconfig
mountPath: /fluentd/etc/
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: dockercontainerlogdirectory
mountPath: /var/log/pods
readOnly: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: dockercontainerlogdirectory
hostPath:
path: /var/log/pods
- name: fluentconfig
configMap:
name: fluentdconf
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: fluentdconf
namespace: default
data:
fluent.conf: |
<label @FLUENT_LOG>
<match fluent.**>
@type null
</match>
</label>
#region kubernetes metadata
<filter kubernetes.**>
@type kubernetes_metadata
</filter>
#endregion
#Enable this for debugging purposes
# <match **>
# @type stdout
# </match>
#region herald logs filters
<source>
@type tail
path /var/log/containers/herald*.log
pos_file /var/log/herald.log.pos
tag kubernetes.*
read_from_head true
format json
<parse>
@type cri
<parse>
@type json
time_key time
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S
keep_time_key true # if you want to keep "time" field, enable this parameter
</parse>
</parse>
</source>
<match kubernetes.var.log.containers.**herald**.log>
@type elasticsearch
host 192.168.10.120
port 31000
logstash_format true
logstash_prefix herald-logs
logstash_dateformat %Y-%m-%d
</match>
#endregion
#region Falcon logs filters
<source>
@type tail
path /var/log/containers/falconsstateful*.log
pos_file /var/log/falconsstateful.log.pos
tag kubernetes.*
read_from_head true
format json
<parse>
@type cri
<parse>
@type json
time_key time
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S
keep_time_key true # if you want to keep "time" field, enable this parameter
</parse>
</parse>
</source>
<match kubernetes.var.log.containers.**falconsstateful**.log>
@type elasticsearch
host 192.168.10.120
port 31000
logstash_format true
logstash_prefix falcon-logs
logstash_dateformat %Y-%m-%d
</match>
#endregion
#region wright logs filters
<source>
@type tail
path /var/log/containers/wright*.log
pos_file /var/log/wright.log.pos
tag kubernetes.*
read_from_head true
format json
<parse>
@type cri
<parse>
@type json
time_key time
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S
keep_time_key true # if you want to keep "time" field, enable this parameter
</parse>
</parse>
</source>
<match kubernetes.var.log.containers.**wright**.log>
@type elasticsearch
host 192.168.10.120
port 31000
logstash_format true
logstash_prefix wright-logs
logstash_dateformat %Y-%m-%d
</match>
#endregion Kibana
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kibana-np
spec:
selector:
app: kibana
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 5601
nodePort: 30000
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kibana
labels:
app: kibana
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: kibana
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: kibana
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.17.6
#resources:
# limits:
# cpu: 1000m
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
value: http://elasticsearch:9200
ports:
- containerPort: 5601Test-pod:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: counter
spec:
containers:
- name: count
image: busybox
args:
[
/bin/sh,
-c,
'i=0; while true; do echo "This is EFK Stack! $i"; i=$((i+1)); sleep 1; done',
]How to deploy
local-path provisioning
NOTE: making as default storage class
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rancher/local-path-provisioner/master/deploy/local-path-storage.yaml
kubectl patch storageclass local-path -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'Deploy ElasticSearch
kubectl create -f ./elasticsearch/es-sts.yamlDeploy Kibana
kubectl create -f ./kibana/kibana-deployment.yamlDeploy Fluentd
kubectl create -f ./fluentd/fluentd-ds.yaml